In today’s fast-paced development environments, missing or misunderstood requirements can derail entire projects. That’s where requirement traceability is vital. It goes beyond being just a technical task; it serves as a strategic safeguard that makes sure every stakeholder’s need is captured, implemented, and verified. Whether you are dealing with complex systems, regulatory compliance, or agile workflows, mastering traceability can be the key to project success and avoiding costly rework. In this post, we will explain what requirement traceability is, why it matters, and how to implement it effectively.

Requirements Traceability
Requirements traceability is the ability to track and link each requirement throughout the project lifecycle—from origin to implementation and validation. It ensures that every requirement serves a purpose and is fulfilled.
Types of Traceability
- Forward Traceability: From business needs → requirements → design → implementation → testing.
- Backward Traceability: From test cases → implementation → design → requirements → business needs.
- Bidirectional Traceability: Combines both directions for full coverage.
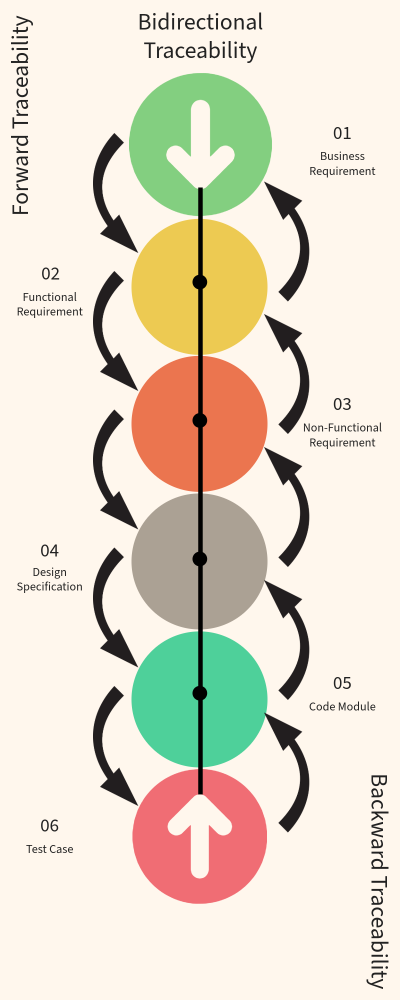
Extended Types of Traceability (for more control)
- Source Traceability: Links requirements to stakeholders who proposed them.
- Design Traceability: Connects requirements to design elements.
- Testing Traceability: Ensures each requirement is covered by test cases.
- Code Traceability: Maps requirements to the actual code implementing them.
- Version Traceability: Tracks changes across different versions of documents or software.
- Release Traceability: Links requirements to specific software releases.
- Risk Traceability: Connects risks to mitigation strategies.
- Business Traceability: Aligns requirements with business goals.
- Quality Traceability: Ensures quality is maintained across design, testing, and implementation.
- Regulatory Traceability: Demonstrates compliance with legal or industry standards.
- Data Traceability: Tracks how data is created, modified, and used.
- Supplier Traceability: Monitors vendor contributions and quality.
- Process Traceability: Follows each step in a process to ensure accuracy.
Each type plays a role in improving transparency, accountability, and quality—especially in industries where compliance and safety are critical.
Traceability Matrix (RTM)
A Requirements Traceability Matrix maps requirements to test cases, ensuring:
- No requirement is missed during testing.
- All features are validated.
- Changes are tracked effectively.
| Requirement ID | Requirement Description | Test Case ID | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| REQ-001 | User login functionality | TC-001 | Passed |
Traceability is especially critical in regulated industries (e.g., aerospace, healthcare) where compliance must be demonstrated.
Want to Know More
More on NFR priorization here.